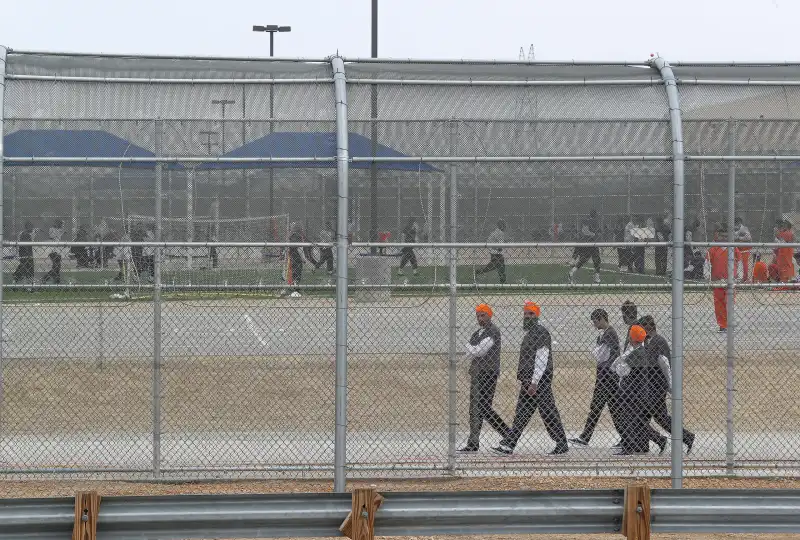
A motion was filed with the Eastern District Court of California on May 18 as part of an ongoing class-action lawsuit against GEO pertaining to the facilities. The filing marked a major escalation in a multipronged campaign being waged by current and former detainees, and outside advocates, to hold ICE and GEO accountable for their mistreatment. It reaffirmed a key demand that detainees in the Mesa Verde ICE Processing Center in Bakersfield and the Golden State Annex in McFarland put forward when they launched a labor strike last year: pay for detained workers commensurate with the prevailing minimum wage in California.
The motion entreated a federal judge to issue a ruling that affirmed the plaintiffs’ contention that the $1-per-day pay detainees receive for labor within GEO’s “Voluntary Work Program” inside Mesa Verde and the GSA violates California’s minimum wage law. The state’s minimum wage stands at $15.50 an hour as of January 2023.
According to the new report “One Dollar A Day: Labor Conditions Within California Immigrant Detention Centers” from the UCLA Luskin Institute on Inequality and Democracy, detained individuals scrub toilets, mop bathrooms, and sweep and perform other maintenance tasks as part of the VWP. The report includes testimony from current and former detainees as well as data and research on commissary expenses, grievances, and information about the working conditions from within the detention centers. “They didn’t have supplies to actually clean,” said one person interviewed for the report. “Whether it was to mop or disinfect the phones or the tables… they just weren’t there… People had to clean the showers a lot of times in their shoes… [Y]our shoes get wet, and we only get one pair of shoes, so that’s unsanitary.”
The same interviewee mentioned the shortage of gloves needed for the work. “Who wants to be scrubbing a toilet with no gloves on? Or clean the showers when you’re dealing with these chemicals,” the individual told the authors of the report. Detainees inside the GSA and Mesa Verde facilities labor under difficult conditions for only a dollar per day, which saves GEO the extra expenses of hiring outside professionals—and increases the corporation’s already bloated bottom line. “GEO is benefiting, because if we don’t do it, they have to pay somebody to do it,” a UCLA report interviewee explained. “And they had to pay somebody good money to come in here and do those jobs.”
While the class-action lawsuit plays out in the Fresno Division of California’s Eastern District Court, individuals confined inside the Bakersfield and McFarland facilities continue to withhold their labor and coordinate with attorneys and immigrant rights’ advocates. They do so despite the retaliation GEO and ICE have repeatedly meted out in response to their refusal to accept the treatment and conditions inside the Central Valley detention centers.
One person interviewed by the UCLA researchers mentioned that staff get angry when detainees raise issues with detention center staff. “And then they want us to get mad and interact with them, just so they have a reason to get us in trouble, because whenever we get a petty ass write-up, it sticks, and we get denied commissary, and you get all these other violations that are put against us. When we write to them we will see no benefits at all,” the detainee said.
The cycle of resistance and retaliation escalated in early 2020, just as the COVID-19 pandemic was beginning to rage across the United States. Dozens of men in Mesa Verde went on multiple hunger strikes in response to the dangerous conditions inside the facility. According to a class-action lawsuit filed in February 2023 by the American Civil Liberties Union of Northern California, hunger strikers called on authorities to release medically vulnerable persons, to stop bringing new people into an already-crowded detention center, and to provide adequate cleaning supplies. In response, the legal complaint alleges, the GEO Group “retaliated against hunger strikers” by withholding sanitation services, commissary access, medically necessary items (including prescription medication and walking canes), contact with attorneys and loved ones, and recreation time.
Two years later, dozens of individuals went on strike against the prison’s $1-a-day labor compensation scheme. ICE’s Performance-Based National Detention Standards set the minimum pay within the Voluntary Work Program at $1 per day. As explained in the “One Dollar a Day” report, in the “70 years since its inception, a provision under an appropriations bill that the 95th United States Congress passed has allowed immigrant workers in detention centers to earn just $1 a day.” According to a 2017 report by Seth H. Garfinkel, the 1978 Appropriations Act passed by Congress codified the remuneration rate, which enables companies like GEO to “compensate workers at $0.13 an hour for as many as eight working hours a day,” while the VWP helps detention centers save about $40 million in labor costs each year. The UCLA report notes that $1 in 1978 is now worth $4.61, and the reimbursement rate has not been adjusted for inflation.
“Detained people are forced to submit to GEO’s $1 per day scheme, the so-called ‘Voluntary’ Activities Program (‘Work Program’), to buy the basic necessities—including food, water and hygiene products—that GEO systematically deprives them of,” states a July 13, 2022, lawsuit filed by two advocacy groups and a Bay Area law firm in the California Eastern District Court.
Mohamed Mousa, an immigrant from Egypt, said that detention center meals typically consist of unappetizing, unsalted beans or unpalatable soy-based meat substitutes. At the time of the interview, he was still detained in the Mesa Verde facility. “It tastes just like newspapers,” Mousa said. “It’s just terrible.”
Detainees in both the GSA and Mesa Verde told the authors of the UCLA report that they found cockroaches in their food. Even when not on hunger strike, people inside won’t touch what the detention centers serve. “Inadequate or inedible food provided by GEO led many detainees to rely on the commissary to supplement some or all of their meals,” the authors of the UCLA report wrote. “Interviewees we spoke to expressed that the commissary was also vital to supplement basic care products that the facility failed to provide, creating additional economic hardship for them.” To afford necessities, detainees thus feel compelled to participate in the VWP, making it less than voluntary.
Likewise, the consequences detainees appear to face for failure to participate in the purportedly voluntary work regime can render it akin to forced labor. For example, participating in the work stoppage almost got one person confined in the Bakersfield immigrant jail transferred, if not for the swift actions of those advocating on behalf of detainee rights.
In August 2022, ICE officials in the San Francisco field office prepared to transfer a striker from solitary to a facility outside of California. “The Facility Administrator stated in a written message to this individual that his efforts to ‘stand up for [his] rights’ would “not be tolerated,’” according to the lawsuit filed in February. ACLU attorneys responded by sending a letter to the field office stating a retaliatory transfer would constitute a violation of the detained person’s First Amendment Rights. ICE returned the man to Mesa Verde shortly thereafter.
The lawsuit from last July alleges other forms of retaliation perpetrated by GEO against detainees on labor strike. Per the suit, GEO stopped allowing entire dormitories outdoor exercise time when individuals inside refused to work, and staff placed strikers in “administrative segregation”—a form of solitary confinement.
According to a September 2022 complaint the ACLU and other organizations sent to the Department of Homeland Security Office of Civil Rights and Civil Liberties, Mousa spent two months in solitary confinement for allegedly posing a risk to the Mesa Verde facility. Rigoberto Hernandez Martinez—a Mesa Verde detainee who joined the strike—was also confined in solitary for over a month due to an alleged security risk after being initially moved there for medical reasons; he was later told he remained in solitary because he participated in the collective action, according to the February lawsuit. “The GEO Group [is] using security as an alibi,” Mousa said.
“Regarding the strike, many described the retaliation by GEO employees, resulting in additional write-ups and denying access to the commissary,” the “One Dollar a Day” report states. Indeed, the authors noted their team “felt it necessary to physically go onsite to Mesa Verde in order to collect the grievances and write-up forms” referenced in the report because of the real fear of repercussion for interviewees.
Retaliation for failure to participate in the VWP also illustrates the not-so-voluntary nature of the labor regime inside the detention centers. The UCLA report states that the filing of grievances significantly increased after the labor strike started, “which detainees described as a response to increased retaliation from GEO officers.” Interviewed individuals said GEO staff used disciplinary write-ups to punish people for participating in the labor strike.
“Write-ups have two impacts on you,” one person explained. “The first is the psychological taste of injustice. So, when you get a write-up for something that is definitely clearly you committed no error, nothing wrong, you didn’t violate anything, you didn’t commit a crime… The mental agony of this is bullshit…. The other aspect is… You can’t even order commissary. You’re gonna have to be starving because they know that you don’t eat their food that they offer.”
The labor strike that began in April 2022 continues, with at least 59 people participating, per sources. Previously, it drew the attention of members of Congress. In September 2022, 16 members of the House and Senate called on ICE to investigate reports of unacceptable conditions and retaliatory behavior directed at detainees in the two California facilities. They also called on DHS to terminate the federal contracts with GEO if the allegations against the facilities could be confirmed.
In December 2022, advocacy groups filed a complaint over unsafe working conditions inside the GSA and Mesa Verde. Following a California Division of Occupational Safety and Health investigation that uncovered multiple state code violations, regulators levied a $104,510 fine against GEO Group.
In an effort to increase the pressure on ICE and GEO, more than 70 detainees at the GSA and Mesa Verde facilities participated in a hunger strike between February 17 and March 24, 2023, demanding their immediate release and the closure of both immigrant jails. A hunger strike support committee made up of advocacy groups including the ACLU, the Asian Law Caucus with Asian Americans Advancing Justice, and the California Collaborative for Immigrant Justice, published a press release in which the men inside described the living conditions as “soul-crushing.”
Milton Mendez, who spent 11 months inside Mesa Verde, said GEO not only failed to provide basic necessities and urgently needed medical care, but the company also maintained intolerable living conditions within the jail. “The bathroom, in the shower, there is mold all over,” Mendez said in a March 17 interview.
In the class-action lawsuit filed this February, attorneys for the plaintiffs rebuked ICE and GEO for violating the First Amendment rights of detained individuals on hunger strike. As a result of the pressure, the detention center relented. “ICE officials and GEO officials [came] to the dorms and referenced the pending litigation,” said Minju Cho, a lawyer with the ACLU, adding that afterwards detention facility staff “ameliorated some of the conditions, including offering the strikers Ensure nutritional shakes to allow them to maintain their strike but not experience death—and allowing them to receive medical care inside the dorm, which would have been a big point of contention. They also restored arts and crafts, law library, barber shop and yard time, all of which had been taken away.”
In response to the hunger strike, GEO deployed retaliatory measures more violent than previously used. According to a press release from the ACLU, on March 7, ICE and GEO employees in full riot gear and wielding batons and pepper spray entered Mesa Verde’s Dorm C to confront weak and depleted hunger strikers. They forcefully removed four strikers from the dorm, handcuffing some and shoving others to the ground. At one point, as Mousa described, “ICE people in camouflage … grabbed [a detainee as if he were] a fucking animal … and they threw him on his face on the ground.”
Aseem Mehta, a legal fellow with AAAJ, said that after several hours, the attorneys for the four individuals who’d been removed from Dorm C received word that their clients were transferred to El Paso, Texas, supposedly for medical care. “Those individuals [had] never before requested medical care [and] showed no signs of acute medical distress,” Mehta said, adding that no explanation was provided as to “why whatever medical care that they purportedly needed could only be accessed in El Paso, Texas,” and not in California. He suspects GEO and ICE might have initiated the transfer to intimidate and punish hunger strikers.
A week after the Mesa Verde raid, ICE and GEO also raided GSA dorms. During that raid, an officer also kneeled on one detainee’s head, injuring his face, according to a March 29 ACLU press release. One hunger striker had to be hospitalized several times as a result of the raid, and GEO transferred three individuals to a Texas facility under medical pretexts, per the press release.
Detainees have learned criticizing the agency and its detention practices can also result in retributive relocation. In February, advocacy groups filed a complaint with the DHS Office of Civil Rights and Civil Liberties that documented ICE’s transfer of an individual in November 2022 after that person and a fellow detainee from another facility authored an op-ed for the San Diego Union-Tribune criticizing conditions of confinement and the agency’s “brutal and excessive use of retaliation.”
In response to the March raids, lawyers from ACLU and other groups filed another emergency motion in federal district court seeking a temporary restraining order to prevent ICE and the GEO Group from retaliating against those on hunger strike. Days after the motion was filed, the seven people transferred to Texas were returned to California.
The anti-carceral group Freedom for Immigrants released a report early this year titled “Trafficked & Toured: Mapping ICE Transfers,” which shows how the transport of human beings functions within “a larger system of punishment of detained individuals for organizing for their rights.”
When reached for comment via email, an ICE spokesperson said that the agency “does not comment on ongoing or pending litigation,” while a GEO spokesperson said via email that the company “has a zero-tolerance policy with respect to staff misconduct.”
“We take our role as a service provider to the federal government with the utmost seriousness and strive to treat all those entrusted to our care with dignity and respect,” the GEO spokesperson said.
The Campaign for Freedom and Abolition Continues
Most detainees who participated in the recent hunger strike—including Mousa—resumed eating food by mid-March, but with help from outside advocates, they are continuing a campaign to break the cycle of violence. Lawsuits by allies at the ACLU, CCIJ, AAAJ, Immigrant Defense Advocates, and others have helped defend the rights of those in custody, stem retaliation, and put pressure on ICE and GEO.
On June 23, the ACLU of Northern California filed another suit, this one against ICE for failing to respond to Freedom of Information Act requests for grievance logs kept at the six agency-affiliated immigrant detention centers in the state.
The ACLU also launched the “California Immigration Detention Database” to track grievances submitted in the state’s immigrant jails. One individual who contributed to the database, Jose Ruben Hernandez Gomez, a former Mesa Verde detainee who was transferred to El Paso after participating in the hunger strike, filed grievances without success while incarcerated in the Central Valley facility, as detailed in an ACLU NorCal report published on June 26. “I’m participating in this project because I want people to know that detention centers are not safe to house human beings,” he told the ACLU.
Of the nearly 250 complaints already in the database, many come from Mesa Verde and date back to the 2023 hunger strike, an ACLU press release explains. “We are committed to working alongside people in detention to expose the cruelty of the immigration detention system—even as ICE fails to come clean about its oversight of facilities marred by systemic neglect and abuse,” said Sana Singh, an ACLU NorCal immigrants’ rights fellow, per the press release. “We hope that, in exposing the futility of the grievance system, this project will show that immigration detention is not a system that can be reformed; it must be dismantled.”
Further augmenting the campaign against ICE, GEO, and their detention regime, recent precedent suggests the lawsuit alleging GEO’s dollar-a-day VWP compensation rate violates the minimum wage requirement in California could prove successful. In 2021, a district court in Washington ordered GEO to give more than 10,000 current and former detainees $17.3 million in backpay for labor they earned $1 to perform each day inside the Northwest ICE Processing Center in Tacoma. Judge Robert Bryan also issued an injunction requiring the company, which pulled in $2.2 billion in revenue that year and receives a quarter million dollars from ICE annually for every detention facility it operates for the agency, to pay detainees participating in the VWP at the Tacoma facility Washington’s minimum wage, now $15.74 an hour.
In addition to using their support networks to exert legal pressure from the outside, those in the GSA and Mesa Verde have inspired and drawn inspiration from detainees elsewhere. Mousa said that hunger strikers in California heard about similar actions in the Tacoma detention center, and in the ICE-affiliated Aurora, Colorado, facility. “We live in [the] same conditions they’re facing all over the place,” he said. “So we’re all supporting each other.” Actions and support for those inside the GSA and MV seemed to have inspired some 300 detainees inside the also GEO-run South Louisiana ICE Processing Center in Basile, Louisiana, to launch their own hunger strike in March.
Organizers and advocates have reason for cautious optimism regarding the possibility of ending for-profit detention for good. In 2019, California Gov. Gavin Newsom signed a bill to phase out private prisons, immigrant detention centers included, but last year an appellate court ruled that the law might be unconstitutional. President Joe Biden voiced support for ending for-profit immigrant detention, but under his administration the Justice Department joined GEO in the suit challenging the law the California legislature passed and Newsom endorsed. A final judgment on the unconstitutionality of the ban was handed down in May 2023, effectively repealing the ban.
Despite these setbacks, current and former detainees and their advocates remain undaunted in their efforts. From inside the GSA in mid-March, Gustavo Flores, a man in his early thirties, said immigration detention “is like waking up in a nightmare.” He hopes to see both ICE and GEO abolished and he and his fellow detainees released. “We’re gonna keep pushing,” Flores said. “If I were to get out [and] win my case… I’m gonna continue advocating.… This is gonna be an ongoing effort that’s going to continue on until our goals are met.”
James Anderson is from Illinois but now resides in Riverside, California. He has taught college courses as an adjunct professor and has freelanced for a number of outlets. He's a member of the IWW Freelance Journalists Union.